Reduced Row Echelon Form Rules
Contents (Click to skip to that department:
- What is Echelon Grade?
- Row Echelon Form
- Reduced Row Echelon Form
- Gaussian Elimination
- Rank of a Matrix
Watch the video for the definitions of echelon, row echelon and reduced row echelon:
Row Echelon and Reduced Row Echelon
Can't run into the video? Click here.
What is Echelon Class?
Echelon form ways that the matrix is in ane of ii states:
- Row echelon class.
- Reduced row echelon class.
This means that the matrix meets the post-obit iii requirements:
- The first number in the row (chosen a leading coefficient) is 1. Note: some authors don't require that the leading coefficient is a 1; information technology could be any number. You may want to cheque with your instructor to come across which version of this rule they are adhering to).
- Every leading 1 is to the right of the one higher up it.
- Any not-zero rows are always to a higher place rows with all zeros.
The post-obit examples are of matrices in echelon form:
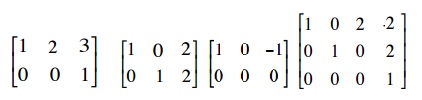
The post-obit examples are not in echelon grade:
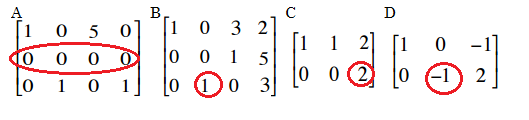
Matrix A does not accept all-zero rows below non-zero rows.
Matrix B has a 1 in the 2nd position on the third row. For row echelon form, it needs to be to the right of the leading coefficient above it. In other words, it should be in the fourth position in identify of the three.
Matrix C has a two as a leading coefficient instead of a 1.
Matrix D has a -1 as a leading coefficient instead of a i.
Another way to call back of a matrix in echelon form is that the matrix has undergone Gaussian emptying, which is a series of row operations.
Uniqueness and Echelon Forms
The echelon grade of a matrix isn't unique, which means there are infinite answers possible when yous perform row reduction. Reduced row echelon course is at the other end of the spectrum; it is unique, which means row-reduction on a matrix will produce the same answer no thing how yous perform the same row operations.
Back to Top.
What is Row Echelon Form?
A matrix is in row echelon form if it meets the following requirements:
- The first non-zero number from the left (the "leading coefficient") is ever to the right of the starting time not-nil number in the row to a higher place.
- Rows consisting of all zeros are at the bottom of the matrix.
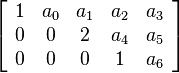
Technically, the leading coefficient can be whatsoever number. However, the majority of Linear Algebra textbooks do state that the leading coefficient must be the number i. To add to the confusion, some definitions of row echelon form state that at that place must exist zeros both above and below the leading coefficient. It's therefore best to follow the definition given in the textbook you're post-obit (or the 1 given to y'all by your professor). If you're unsure (i.e. information technology'due south Sunday, your homework is due and you can't get concord of your professor), information technology safest to utilize 1 as the leading coefficient in each row.
If the leading coefficient in each row is the only non-zero number in that column, the matrix is said to be in reduced row echelon course.
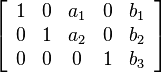
Row echelon forms are ordinarily encountered in linear algebra, when yous'll sometimes exist asked to convert a matrix into this form. The row echelon form can help y'all to meet what a matrix represents and is besides an of import footstep to solving systems of linear equations.
Online Row Echelon Form Figurer
This online calculator volition convert any matrix, and provides the row operations that get yous from stride to pace. The following paradigm (from the Former Rule University Calculator shows how the matrix [01, 00, 59] is reduced to row echelon class with 2 unproblematic row operations:
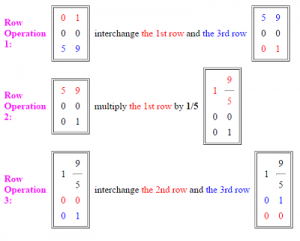
Dorsum to Top.
What is Reduced Row Echelon Form?
Reduced row echelon class is a type of matrix used to solve systems of linear equations. Reduced row echelon course has 4 requirements:
- The first non-nix number in the outset row (the leading entry) is the number 1.
- The 2nd row also starts with the number ane, which is further to the right than the leading entry in the kickoff row. For every subsequent row, the number 1 must be farther to the right.
- The leading entry in each row must be the only non-aught number in its cavalcade.
- Any non-zero rows are placed at the lesser of the matrix.
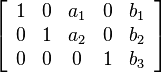
Transformation of a Matrix to Reduced Row Echelon Course
Whatsoever matrix tin be transformed to reduced row echelon course, using a technique called Gaussian elimination. This is particularly useful for solving systems of linear equations. Near graphing calculators (like the TI-83) have a rref function which will transform a matrix into a reduced row echelon form. Encounter: This article on the Colorado State Academy website for instructions on using the TI-89 and TI-83 to calculate reduced row echelon form.
This online figurer on the Erstwhile Dominion Academy website transforms a matrix that you input to reduced row echelon form.
Adding by manus requires cognition of simple row operations, which are:
- Interchange one row with another.
- Multiply i row by a non-nix constant.
- Replace one row with: one row, plus a constant, times another row.
In addition, information technology isn't enough merely to know the rules, you have to be able to look at the matrix and make a logical decision nearly which rule y'all're going to use and when. You're trying to get the matrix into reduced row echelon form, so you lot'll also demand to refer to the four requirements at the kickoff of this article. If yous have to catechumen a matrix to reduced row echelon form by hand, it's a good idea to use one of the calculators in a higher place to check your work. In fact, of you lot use the ODU online reckoner, it will even provide the row operations for you. The prototype below is the figurer's conversion of the matrix [204,923]:

Dorsum to Top.
What is Gaussian Elimination?
Gaussian elimination is a manner to find a solution to a system of linear equations. The basic idea is that y'all perform a mathematical operation on a row and go on until only one variable is left. For example, some possible row operations are:
- Interchange any 2 rows
- Add two rows together.
- Multiply one row by a non-nada constant (i.eastward. i/three, -1, five)
You tin too perform more than than one row functioning at a time. For example, multiply 1 row by a constant so add the result to the other row.
Following this, the goal is to end upward with a matrix in reduced row echelon form where the leading coefficient, a 1, in each row is to the right of the leading coefficient in the row higher up information technology. In other words, you need to get a 1 in the upper left corner of the matrix. The next row should have a 0 in position ane and a i in position 2. This gives yous the solution to the system of linear equations.
Gaussian Elimination Example
Solve the following system of linear equations using Gaussian elimination:
- x + 5y = vii
- -2x – 7y = -5
Step 1: Convert the equation into coefficient matrix form. In other words, simply accept the coefficient for the numbers and forget the variables for now:
![]()
Step ii: Plow the numbers in the bottom row into positive by adding 2 times the first row:
![]()
Pace 3: Multiply the 2d row by 1/3. This gives you your second leading 1:
![]()
Pace iv: Multiply row ii by -5, and then add this to row one:
![]()
That'due south it!
In the kickoff row, you have x = -eight and in the second row, y = 3. Note that x and y are in the aforementioned positions equally when y'all converted the equation in footstep one, so all you have to do is read the solution:
![]()
Back to Top.
What is the Rank of a Matrix?
The rank of a matrix is equal to the number of linearly contained rows. A linearly independent row is one that isn't a combination of other rows.
The following matrix has two linearly independent rows (one and 2). However, when the third row is thrown into the mix, you lot tin can see that the first row is now equal to the sum of the second and third rows. Therefore, the rank of this item matrix is 2, as there are just two linearly independent rows.
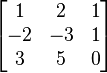
The matrix rank will always be less than the number of non-zero rows or the number of columns in the matrix. If all of the rows in a matrix are linearly contained, the matrix is full row rank. For a square matrix, it is only full rank if its determinant is non-cipher.
Figuring out the rank of a matrix by trying to determine by sight but how many rows or columns are linearly contained tin can be practically impossible. An easier (and perhaps obvious) style is to convert to row echelon class.
How to Find the Matrix Rank
Finding the rank of a matrix is simple if you lot know how to find the row echelon matrix. To discover the rank of whatsoever matrix:
- Notice the row echelon matrix.
- Count the number of non-zero rows.
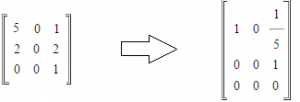
The above matrix has been converted to row echelon form with two non-goose egg rows. Therefore, the rank of the matrix is 2.
You tin also discover an fantabulous conversion tool on the Old Dominion University website.
Back to Superlative.
References
Everitt, B. Southward.; Skrondal, A. (2010), The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics, Cambridge University Press.
Gonick, L. (1993). The Drawing Guide to Statistics. HarperPerennial.
Searle, S. (2017). Matrix Algebra Useful for Statistics (Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics) second Edition. Wiley.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Need help with a homework or exam question? With Chegg Study, you can get step-by-stride solutions to your questions from an practiced in the field. Your start 30 minutes with a Chegg tutor is gratis!
Comments? Need to postal service a correction? Please Contact Us .
Reduced Row Echelon Form Rules,
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/matrices-and-matrix-algebra/reduced-row-echelon-form-2/
Posted by: christoffersothemnioncy64.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Reduced Row Echelon Form Rules"
Post a Comment